In today’s interconnected world, computer networking serves as the backbone of modern society, enabling seamless communication, data exchange, and resource sharing. From browsing social media to managing multinational corporations, networking is integral to powering the digital age. This article delves into how computer networking functions, its various components, and its pivotal role in transforming the way we live, work, and connect.
The Basics of Computer Networking
At its core, computer networking refers to the interconnection of computing devices—such as computers, servers, and smartphones—to share information and resources. These devices communicate using protocols, which are standardized rules ensuring that data is transmitted efficiently and securely. Networking can occur on different scales:
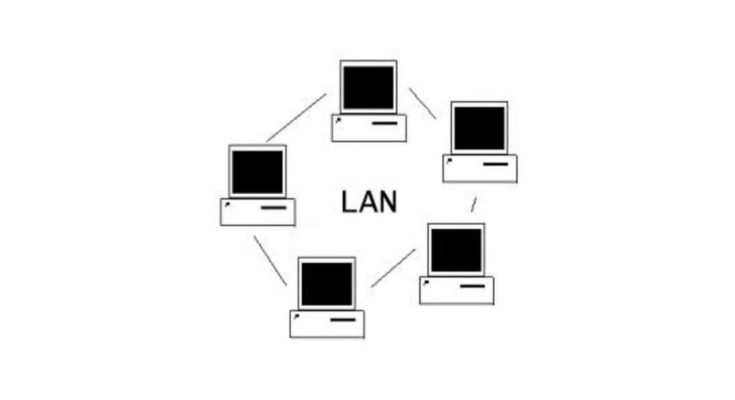
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Connecting devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school.
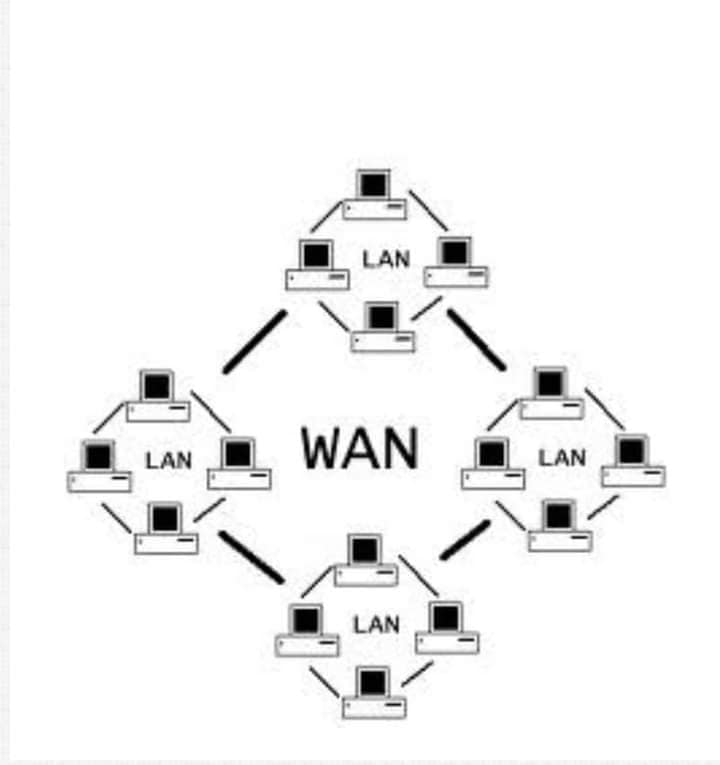
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): Spanning larger geographical areas, often consisting of interconnected LANs.
- The Internet: The largest WAN, connecting millions of private, public, academic, and business networks worldwide.
Key Components of Networking
Several elements work together to create functional and efficient networks. These include:
- Hardware
- Routers: Direct data packets between networks.
- Switches: Manage data traffic within a local network.
- Servers: Store, process, and manage network resources.
- End Devices: Computers, smartphones, IoT devices, and more.
- Software
- Operating Systems: Manage communication between hardware components.
- Applications: Facilitate tasks like email, file sharing, or video conferencing.
- Protocols
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The foundational protocol suite of the Internet.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Used for accessing web pages.
- SMTP/POP3: For sending and receiving emails.
How Networking Transforms Key Industries
Computer networking has revolutionized almost every sector by improving efficiency, fostering innovation, and enabling global collaboration. Below are some key industries where networking plays a transformative role:
1. Education
Networking has expanded access to education through e-learning platforms and virtual classrooms. Students can connect to resources worldwide, attend online lectures, and collaborate on projects in real-time. Networking tools such as video conferencing, cloud storage, and online forums make learning more interactive and accessible.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, networking facilitates telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and remote monitoring systems. Patients can consult doctors online, while healthcare providers can share vital data securely over networks. Networking also powers medical research by enabling the sharing of large datasets globally.
3. Business and Commerce
From small startups to multinational corporations, businesses rely on networking for operations. Online transactions, cloud-based software, and remote work are all made possible by robust networks. Networking has also driven the rise of e-commerce, connecting buyers and sellers across continents.
4. Entertainment
Streaming platforms, online gaming, and social media owe their existence to computer networking. These platforms require high-speed networks to deliver content seamlessly to millions of users simultaneously, ensuring an enjoyable experience.
5. Government and Public Services
Networking enables efficient governance through digital public services, online tax filing, and e-governance portals. Governments also use networks for surveillance, security, and disaster management.
Networking in Everyday Life
For the average user, networking has become indispensable. Here are a few examples of how networking powers daily activities:
- Internet Access: Whether at home or on the go, networks enable instant access to information, communication tools, and entertainment.
- Smart Homes: IoT devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and voice assistants connect via networks to create efficient and automated living environments.
- Social Connectivity: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram use networks to connect billions of users worldwide, fostering global communication.
The Evolution of Networking
Computer networking has undergone remarkable evolution since its inception. Here’s a brief timeline:
- The 1960s: The first computer networks, like ARPANET, laid the groundwork for the Internet.
- The 1980s: The development of Ethernet and TCP/IP protocols made networking more accessible and reliable.
- The 1990s: The rise of the World Wide Web revolutionized how information was accessed and shared.
- The 2000s: Wireless networking (Wi-Fi) became mainstream, enabling mobility and convenience.
- Today: Technologies like 5G, cloud computing, and IoT continue to push the boundaries of networking, making it faster, smarter, and more integrated.
Challenges in Networking
Despite its many advantages, networking faces challenges that require ongoing innovation and vigilance:
- Security Threats: Cyberattacks, data breaches, and malware are constant concerns. Implementing robust security protocols is essential.
- Bandwidth Demands: The increasing volume of data generated by users and devices strains network capacity.
- Latency Issues: Low latency is critical for real-time applications like gaming, video conferencing, and autonomous vehicles.
- Scalability: Networks must adapt to accommodate the growing number of connected devices.
The Future of Networking
The future of computer networking is poised to be transformative, driven by advancements in technology:
- 5G Networks: Offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, 5G will revolutionize industries like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and virtual reality.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered networking solutions can optimize traffic, predict outages, and enhance security.
- Edge Computing: Decentralizing data processing to the network’s edge reduces latency and improves efficiency.
- Quantum Networking: Though in its infancy, quantum networking promises ultra-secure communications and unparalleled data transmission speeds.
Conclusion
Computer networking is the lifeblood of the digital world, enabling global connectivity and powering innovations that shape our lives. From personal convenience to industrial advancements, networking is at the heart of technological progress. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so will the networks that sustain it, ensuring a more connected and efficient future for all.